
Trust Tablet
Salt Composition
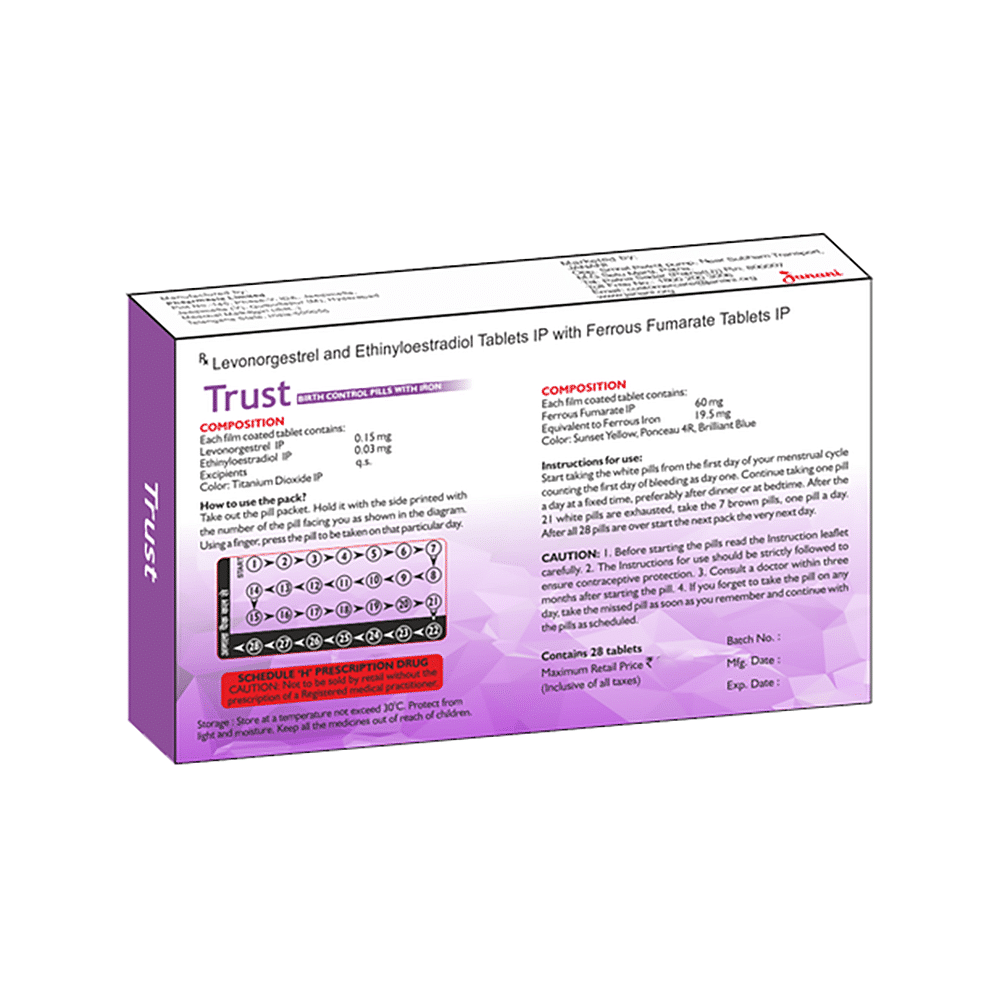
Levonorgestrel (0.15mg) + Ethinyl Estradiol (0.03mg) + Ferrous Fumarate (60mg)
Key Information
Short Description
Trust Tablet is a combined oral contraceptive pill used for contraception (to prevent pregnancy). It is a combination of progestin (levonorgestrel) and an estrogen (ethinyl estradiol).
Dosage Form
Tablet
Introduction
Trust Tablet can be taken with or without food. Take with food if it causes an upset stomach. It should be taken as per your doctor's advice. The dose and how often you take it depends on what you are taking it for. Your doctor will decide how much you need to improve your symptoms. Swallow the tablets whole with a glass of water. You should take this medicine for as long as it is prescribed for you. Headache, nausea, stomach upset, and breast pain are some common side effects of this medicine. If these bother you or appear serious, let your doctor know. There may be ways of reducing or preventing them. You might experience spotting or bleeding between menstrual periods or missed periods. Consult with your doctor if this occurs frequently or persists longer. Before taking this medicine, let your doctor know if you smoke and are over 35 or if you have ever had a heart attack or have cancer of uterus/cervix or vagina. Your doctor should also know about all other medicines you are taking as many of these may make this medicine less effective or change the way it works. Do not take the medicine if you are pregnant already or breastfeeding.
Directions for Use
Take this medicine in the dose and duration as advised by your doctor. Swallow it as a whole. Do not chew, crush or break it. Trust Tablet may be taken with or without food but it is better to take it at a fixed time.
Safety Information
Side Effects
Headache Nausea Stomach upset Breast pain
Breastfeeding Warning
Do not take the medicine if you are breastfeeding.
Pregnancy Warning
Do not take the medicine if you are pregnant already.
How it works
Trust Tablet is a combined oral contraceptive pill. It works by preventing the release of egg (ovulation) and affecting sperm movement in the womb to prevent its union with the egg. It also changes the lining of the womb and renders it unsuitable for pregnancy.


