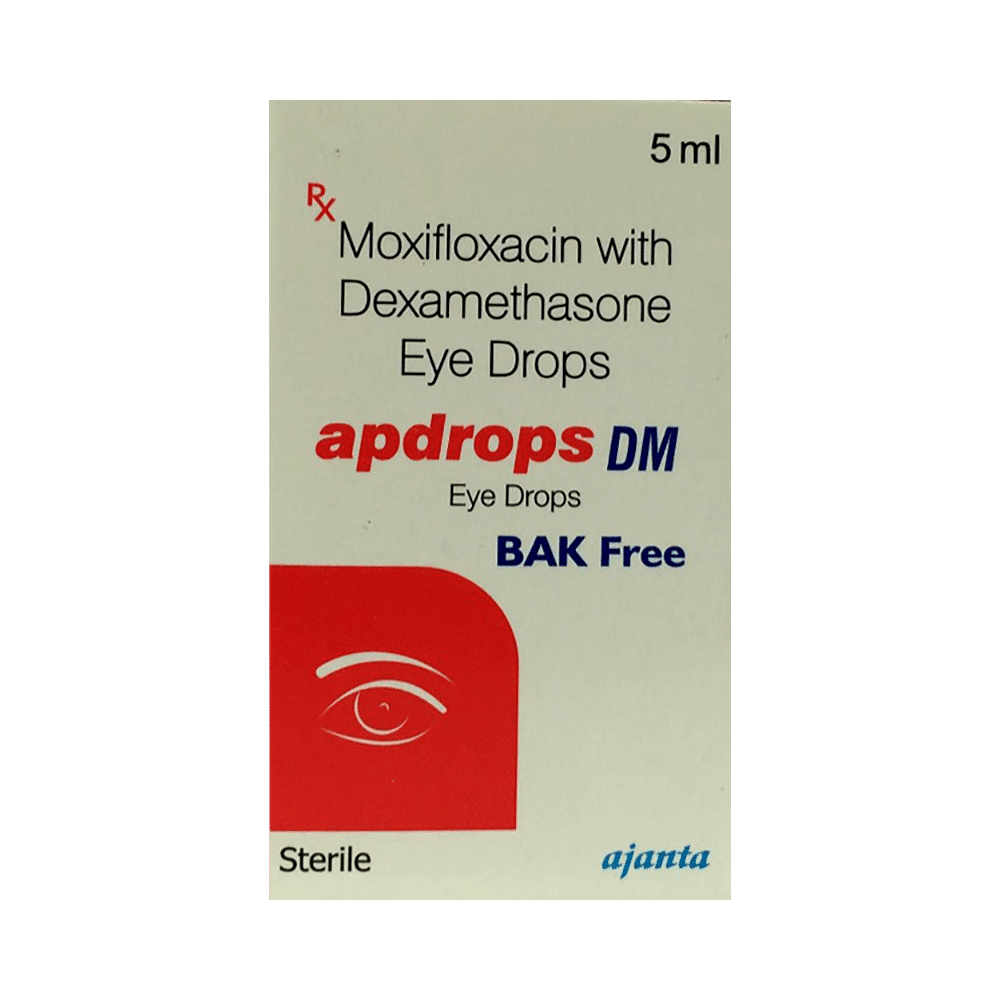

Apdrops DM Eye Drop
Manufacturer
Ajanta Pharma Ltd
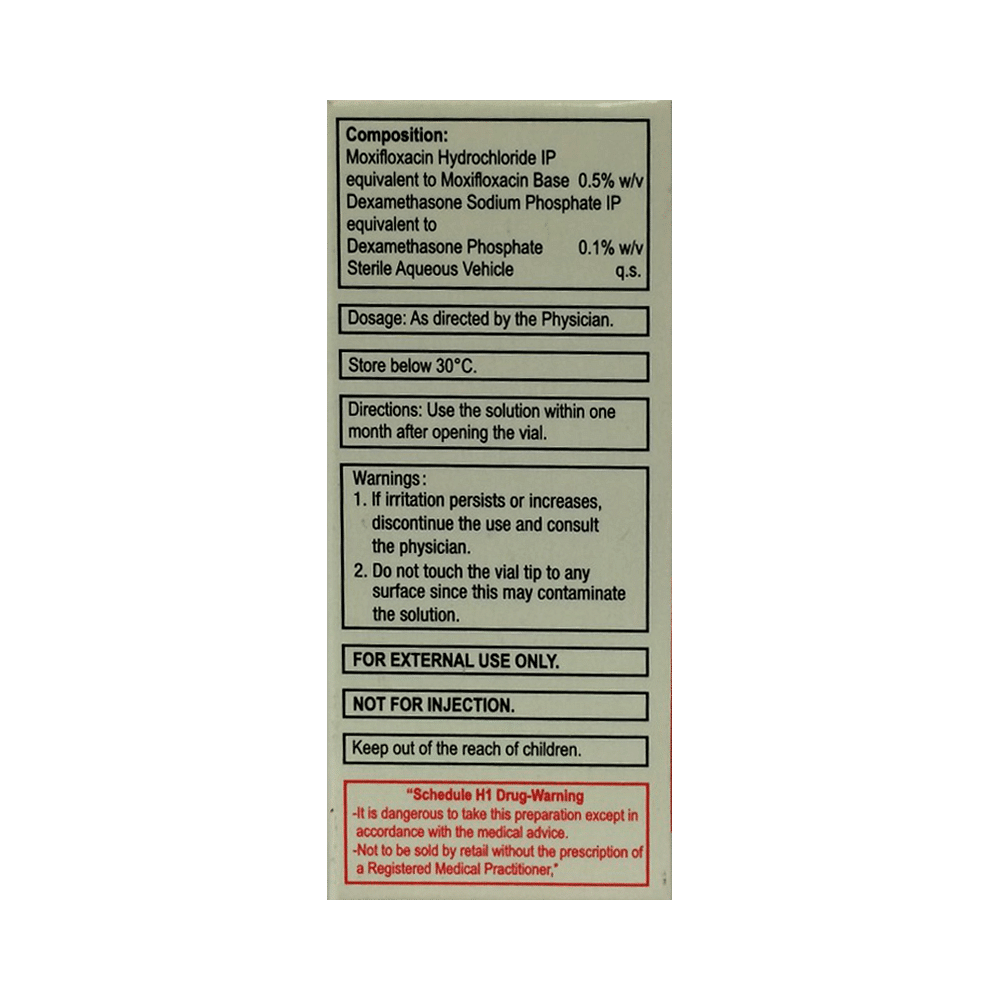
Salt Composition
Moxifloxacin (0.5%w/v) + Dexamethasone (0.1%w/v)
Key Information
Short Description
Apdrops DM Eye Drop is a prescription medicine used to treat bacterial eye infections, relieving redness, itching, and swelling.
Dosage Form
Eye Drop
Introduction
Apdrops DM Eye Drop is to be used only in the affected eye in the dose and duration as advised by the doctor. Wash your hands before using this medicine. It is advised to check the label for directions before use. Do not skip any doses and finish the full course of treatment even if you feel better. Stopping the medicine too early may lead to the infection returning or worsening.
Directions for Use
This medicine is for external use only. Use it in the dose and duration as advised by your doctor. Check the label for directions before use. Hold the dropper close to the eye without touching it. Gently squeeze the dropper and place the medicine inside the lower eyelid. Wipe off the extra liquid.
How it works
Apdrops DM Eye Drop is a combination of two medicines: Moxifloxacin and Dexamethasone. Moxifloxacin is an antibiotic which prevents bacterial cells from dividing and repairing thereby killing the bacteria. This treats your eye infection. Dexamethasone is a steroid which blocks the production of certain chemical messengers (prostaglandins) that make the eye red swollen and itchy.
Quick Tips
Do not skip any doses and finish the full course of treatment even if you feel better. Do not touch the tip to any surface to avoid contamination. Wait for at least 5-10 minutes before delivering the next medication to avoid dilution. It may cause short term blurring of vision when first used. Use caution before driving or using machines. Do not wear contact lenses until your infection clears up.
Related Medicines

Mahaflox-D Eye Drops
Moxitak D Eye Drop

Moxigram-DM Eye Drop

Moxisurge-D Eye Drop

Moxoft D Eye Drop
Moxicip D Eye Drop

Moximax D Eye Drop

Myticom Eye Drop

Moxiblu-D Eye Drop

Finemoxi-D Eye Drop
Frequently asked questions
How long does Apdrops DM Eye Drop take to show its effects?
Apdrops DM Eye Drop typically starts to show its effects soon after application. However, it may take a few days to effectively eliminate the infection and achieve optimal results.
Can I discontinue using Apdrops DM Eye Drop once I start feeling better?
No, it is essential to complete the full course of treatment with Apdrops DM Eye Drop, even if you experience symptom relief before the infection is fully cleared. Stopping treatment prematurely may lead to incomplete eradication of the infection.


